About the owner
The business will be a sole proprietorship business, and Jama Mohamed Warsame will own it. The basic information of the business is given below-
| Business name: | Diabetic Centre |
| Owner(s) name: | Jama Mohamed Warsame |
| Business address and postcode: | Hargaisa, Somaliland |
| Business telephone: | N/A |
| Business email address: | hargaisasomaliland@gamil.com |
| Home address and postcode | Hargaisa Somaliland |
Table 1: Basic information about the business
Skills and expertise of the owner
The owner is vastly experienced in the health care sector. He has the experience of working in the health care sector of the United Kingdom, and he has been working in the UK health care sector for more than 15 years as a Clinician. Apart from this, Mr Jama Mohamed Warsame was educated and trained in the United Kingdom. Thus, the owner possesses the necessary expertise, skills and relevant experience to run the Diabetic Centre properly.
Business Overview
Purpose
The business founder has initiated the industry to educate the patients about diabetics and their treatment and promote self-care management so that they can take care of themselves without frequently going to diabetic centres during the hard times of their health.
Mission
The business has been started with a few missions keeping in mind. It wants to serve its customer’s patient-centred affordable treatment facilities and give hopes to live a better, healthier and happier life. Most importantly, it aims at supporting and empowering its patients of diabetes type 2 patients to overcome their diseases by providing necessary diets and educating them with a proper lifestyle.
Management
The Diabetic centre will have the following command and personnel-
Owner | Jama Mohamed Warsame |
Medical team |
|
Support staff |
|
Table 2: Management of the business
SWOT analysis
Through SWOT analysis, the proposed business’s internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. The proposed Diabetic Centre’s SWOT analysis is discussed here.
The strengths are the most significant components for the business to sustain and grow in such a country. The business owner has more than 15 years of work experience in the UK, and the management is planning to hire two medical doctors, 1 Dietician, 1 Nurse, 2 laboratories, and 1 pharmacist for its medical operation. And it also has collaboration with King’s College London for offering DNA analysis for its customers. Thus, the strengths of the business will be very effective for the organisation to sustain.
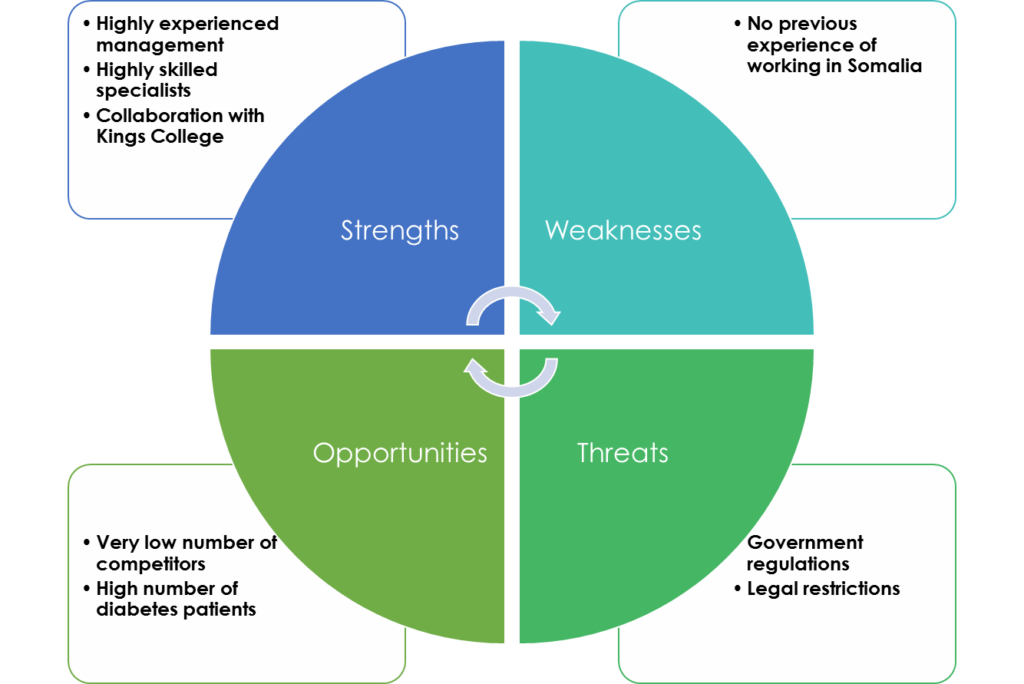
However, the management of the company does not have any prior experience of working in Somalia. Therefore, it is their weakest point in operating in Somalia. Nevertheless, working in Somalia does also bring many opportunities. As it is an impoverished and undeveloped country, there are not many diabetic care centres in Somalia, but there are many diabetic patients, and the number is overgrowing. Therefore, these geographical and national factors bring many opportunities for the business. Despite such opportunities, there is a threat that government regulations and restrictions might be imposed on the company, which might thwart the progress.
STP analysis
STP analysis includes segmentation, targeting and positioning strategy analysis for the proposed business. The STP analysis for the Diabetic Centre is discussed below.
Segmentation & targeting
The proposed business’s overall market has been segmented in three ways: age, income level, and customer types. The segmentation and targeting and their justification are discussed below.
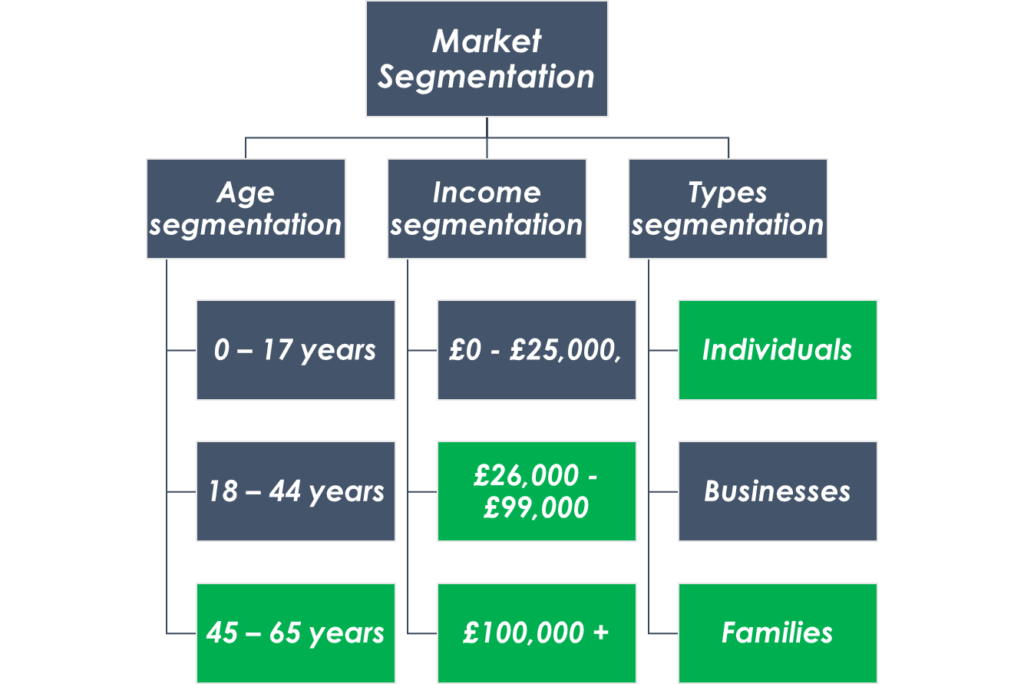
The overall population has been segmented into three age categories. The categories are 0-17 years, 18-44 years, and 45-65 years. The promotional activities will primarily be done approaching the people aged more than 45 years as this group has the highest track record of being diabetes patients. However, the group ageing 18-44 will also be under consideration. Primarily, the diabetic centre will be targeting the people whose earnings level is £26,000 or more. Because diabetes treatment requires a certain amount of expenditure, the customers also need to have a minimum earning status to bear the costs. Lastly, not surprisingly, individuals and families are being targeted.
Positioning
As it is an entirely new diabetic centre cum business, the positioning strategy would be crucial for the organisation to target, reach, and have enough customers to profit and sustain. The company / diabetic centre must position itself with its top-quality treatment service, experienced and professional doctor, and its dedication to providing hope and effort to make people self-sufficient to lead a healthy and problem-free life.
Marketing mix analysis
Marketing mix analysis includes the analysis of the 4Ps of a business or organisation. The 4Ps have Products, Price, Place and Promotion. The marketing mix analysis for the proposed business is discussed here.
The business is expected to offer mainly two services. The first and foremost service is to provide treatment and consultancy to type 2 diabetes patients. And secondly, the centre will provide special health check-up facilities for its clients. Thirdly, the business is expected to offer DNA test facilities for different purposes in collaboration with King’s College London.
Price
Since the organisation is about to start its business, it is expected to use a Market Penetration pricing strategy to enter and reach as many clients as possible. The pricing for the three products are as follows-
Particulars | (2019/20) (£) | (2020/21) (£) | (2021/22) (£) |
Diabetes patient visit | 15.0 | 18.0 | 20.0 |
Health check-ups | 50.0 | 55.0 | 60.0 |
DNA tests | 135.0 | 140.0 | 145.0 |
Table 3: Pricing of different products
Place
The business is expected to operate in Somalia.
Promotion
The promotion strategy will be crucial for the diabetic centre as it will be operating for the first time in the Somalia region. Therefore, the organisation must have a proper promotional strategy to reach its desired target audience. The new business will be using newspapers, banners and posters as an offline medium to promote its business. And it will use email marketing, website, and social media marketing for online promotion.
Value chain of the business
The value chain of the business would comprise primary activities and support activities. The primary activities include inbound logistics, operations, promotion and service of the firm.
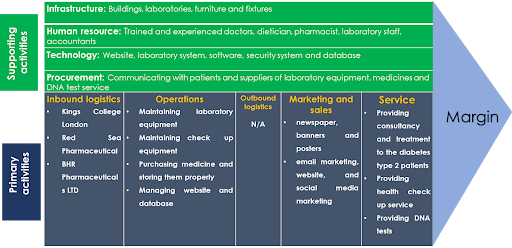
Inbound logistics include the names of the other organisations with whom the Diabetic Centre will be partnering to have medicine, laboratory equipment and DNA test support. Operations include the regular activities that the staff will provide its primary services to its clients. The marketing and services have already been discussed earlier in this report.
The infrastructure of the business will include its building, apartment, laboratories, furniture and fixtures. The technological resources include websites, laboratory systems, security systems etc. Procurement activities include procuring medicine, laboratories equipment and DNA test facilities.
Legal issues
The diabetic centre will be operating in Somalia, but it has many connections and activities in the UK. Therefore, the diabetic centre will have to abide by the rules and regulations of both countries. The diabetic centre will be regulated under the statutes and laws of the ministry of health. Besides, it will also have to abide by the regulations of local laws and authorities of Somalia. It will have to take a licence from the relevant authorities and register for importing its necessary materials from the suppliers.
Financials
Financials include the preparation of Pro-forma financial statements for the proposed business. In this case, the Pro forma Income statement for the next three year, Assets, and total capital required for the first will be prepared with justification. The total assets of the business for the first will be as follows-
Item required | Price (£) | Yearly amount |
Furniture and Fittings | 3,000 | 3,000 |
Premises/Warehouse | 12,000 | 12,000 |
Equipment | 35,000 | 35,000 |
Transport & Vehicles – Car, Van, Truck | 7,000 | 7,000 |
Hardware & Software | 3,000 | 3,000 |
Security Systems and Surveillance Cameras | 300 | 3,600 |
Websites and Social Media Development | 2,000 | 2,000 |
Displays | 500 | 500 |
Others (Please mention) | 200 | 2,400 |
Total | 68,500 | |
Table 3: Assets size of the Diabetic Centre
In preparing the business’s Pro-forma income statement, it is necessary to assume the sales price per unit, the total number of sales units, and material costs per unit. As the diabetic centre will be serving two primary services, the pro forma statement has been prepared based on those two products. The selling price for the diabetes patient visit has been set up to 15 pounds per visit. And this price will increase over the upcoming years. It will be 18pound and 20pound for the next two years. The material costs for diabetes patients include only the medicine provided to them from the diabetic centre, and this has been set at 5pound per patient for the first year. It will be 5.5pound and 6pound for the following two years, respectively. The health check-up’s selling price has been set at 50pounds, 55pounds and 60 pounds for the first three years, respectively. The DNA test’s selling price has been set at 135 pounds for the first year, and it will be 140pounds and 145pounds for the next two years, respectively.
Pro forma Income Statement For Diabetic Centre For the first 3 years of operation | |||
Particulars | Year 1 (2019/20) | Year 2 (2020/21) | Year 3 (2021/22) |
Diabetes Patients visit (Estimated Units) | 3,500.0 | 4,000.0 | 4,700.0 |
Selling price per unit | 15.0 | 18.0 | 20.0 |
Materials cost per unit (only medicine costs) | 5.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 |
Total Revenue from Diabetes patients | 52,500.0 | 72,000.0 | 94,000.0 |
Total Cost of service provided Patient visit | 17,500.0 | 22,000.0 | 28,200.0 |
Gross profit from diabetes patients visit | 35,000 | 50,000 | 65,800 |
Health Check-up (Estimated Units) | 1,500.0 | 2,000.0 | 3,000.0 |
Selling price per unit | 50.0 | 55.0 | 60.0 |
Materials cost per unit (Laboratory maintenance) | 42.0 | 42.0 | 47.0 |
Total Revenue from health check-up | 75,000 | 110,000 | 180,000 |
Cost of service provided health check-up | 63,000 | 84,000 | 141,000 |
Gross profit from health checkups | 12,000 | 26,000 | 39,000 |
DNA tests (Estimated Units) | 55.0 | 60.0 | 65.0 |
Selling price per unit | 135.0 | 140.0 | 145.0 |
Materials cost per unit | 120.0 | 122.0 | 125.0 |
Total Revenue from DNA tests | 7,425 | 8,400 | 9,425 |
Cost of service provided DNA test | 6,600 | 7,320 | 8,125 |
Gross profit from DNA test | 825 | 1,080 | 1,300 |
Total Gross profit | 47,825 | 77,080 | 106,100 |
Selling expenses | |||
Salaries & Social Insurance & Commissions | 8,000 | 10,000 | 12,000 |
Motor Car Expenses | 7,000 | – | – |
Advertising | 1,000 | 1,000 | – |
Total Selling expense | 16,000 | 11,000 | 12,000 |
Operating and administrative expenses | |||
Legal Fees | 1,200 | 1,200 | 1,200 |
Subscriptions and Donations | 600 | 600 | 600 |
Rent Expenses | 12,000 | 12,000 | 12,000 |
Electricity and Water | 3,600 | 3,600 | 3,600 |
Printings & Stationeries | 1,200 | 1,200 | 1,200 |
Telephone | 2,400 | 2,400 | 2,400 |
Repairs and Renewals | 3,600 | 3,600 | 3,600 |
Cleaning Expenses | 1,200 | 1,200 | 1,200 |
Overseas Travelling | 2,000 | 3,000 | 4,000 |
Computer Expenses | 1,200 | 1,200 | 1,200 |
Security Services | 3,600 | 3,600 | 3,600 |
Total | 32,600 | 33,600 | 34,600 |
Total Selling and administrative expense | 48,600 | 44,600 | 46,600 |
Net Profit | (775) | 32,480 | 59,500 |
Table 4: Pro-forma income statement
The number of patient visits for the first year for diabetes check-up and medicine purposes has been estimated at 3500, assuming around 10 patients every day on average for the first year. As the year passes, the number of patients visiting the diabetic centre will increase. It will be 4000 in the second year and 4700 in the third year considering the promotional aspects and reputation of a well-managed diabetic centre.
The first year will not be profitable for the business, considering substantial capital costs and fewer sales. Hence, it is expected to experience a net loss of (775) pounds in the first year in the first year. However, from the second year, it will start earning profit. The diabetic centre is expected to make a net profit of 32,480 pounds and 59,500 pounds in the following 2 years.
The total start-up capital that the business will be required for the first year would include total assets and total working capital, along with other expenses that it will have to bear for the first year. Thus, total start-up capital requirement = total assets + material costs + selling expenses + administrative expenses.
Particulars | Amount in pound |
Total assets | 68,500 |
Total Cost of service provided Patient visit | 17,500 |
Cost of service provided health check-up | 63,000 |
Cost of service provided the DNA test | 6,600 |
Total Selling and administrative expense | 48,600 |
Total Startup capital requirement | 204,200 |
Table 5: Start-up capital requirement





