Introduction
For analysis and case study, Virgin Atlantic Airlines and Age UK will be used in the unit. Both the organisations are highly reputed and based in the UK. Virgin Atlantic Airlines is an airline business, and Age UK is an organisation working to better older people. Age UK is the largest charity in the UK.
1.1 describe the type of business, purpose, and ownership of two contrasting businesses
Being an international business Virgin Atlantic Airlines operates in more than 15 countries of Asia, Africa, Europe and North America. On the other hand, Age UK acts in the UK only. It is a local not-for-profit business in the UK as a not for profit organisation; Age the UK does not make a profit and freely keeps that like Virgin Atlantic Airlines. They use their profit again for the organisation. No money comes out of the organisation to the hands of owners. Both the businesses are service-based organisations and participate in the tertiary sector.
Virgin Atlantic Airlines aims to arrange a safer and cheap journey by air for the consumers. The company targets customers who want to make the journey at a lower cost. Age UK is more committed to its consumers. It works without any profit and creates a smooth life-ending and fulfilling the wishes of older adults in their living and after death.
Both businesses are privately operated. Virgin Atlantic Airlines is a public limited company, and Age UK is a charitable trust. According to the charities act 1992 and 1993, the charity trustees have a greater degree of liability to the customers. As a limited company, Virgin Atlantic Airlines needs lots of formalities, regulations to maintain. The original owners may even lose control. Age UK cannot raise equity investment as a charity.
1.2 describe different stakeholders who influence the purpose of two contrasting businesses
Stakeholders are part of the organisation and continuously affect business sectors with their participation and interest in different businesses. Customers affect businesses by their power to control business’s profit. Virgin Atlantic Airlines needs more commitment to the customers as their profit can decline due to customer dissatisfaction. The purpose and objective of both organisations are achieved by their employees. The employees work for certain benefits from the organisation. Any of their dissatisfaction will create a problem in the smooth achievement of objectives. Customers directly interact with employees. The employees get supply from suppliers (Mitra and Singh, 2010). Employees and suppliers are two groups who arrange raw materials and render services to customers after development. So the groups can influence company reputation. As employees are involved, the trade unions will demand facilities from the organisation. Owners own businesses; for Virgin Atlantic Airlines, owners will require profit. The profit is also suitable for stockholders as they invest. On the other hand, for age UK owners have the right to get the reputation at least. Governments are providing facilities directly or indirectly. So they can ask businesses for tax repayment properly. For Age UK, the government can demand simple operation and exemplary service to the state’s citizens. Trade unions are influenced by laws and protest. They try to bring more and more facilities for employees. But it increases the cost for businesses. Virgin Atlantic Airlines is also influenced by the government by different laws and regulations. Government influences to create a fairground for business and keep up all the rights of consumers.
2. Describe how two businesses are organised
How a business is organised can be understood by its structure. The structure is the way the employees of a business run operations from their position. For example, the business operation of Age UK is done by a flatter organisational structure. According to the system, employees have a free flow of upward and downward communication with the upper management level. On the other hand, Virgin Atlantic Airlines operates by flat arches. Two flat team members stay at the top of management in the organisation.
The organisational structure can also be divided into five types. They are; matrix, functional, product, customer and geographic.
Age UK has a functional organisation structure. The organisation operates only in the UK. So it is straightforward for the organisation to control all the activities by the available heads. The heads of different departments manage its operations, marketing, HR, production and other activities (Atkinson and Nilles, 2010). The director keeps account of all these heads. The structure is represented below in a figure.
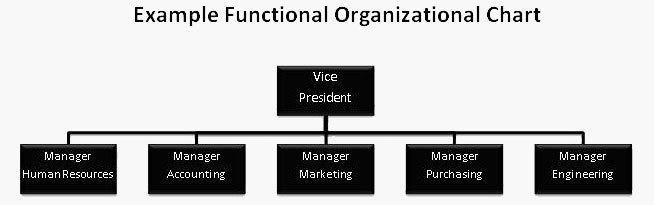
Virgin Atlantic Airlines runs its operation all over the world. It has area managers to watch over all the activities in a region. The organisation runs on a combination of geographic and functional organisational structure. Under an area manager of a region, some other department heads run the business in a useful manner (Morgan, 2010). The Area Manager reports to the company director. But for the operational heads, the area manager is the company director. The structure of Virgin Atlantic Airlines is presented below in a figure.
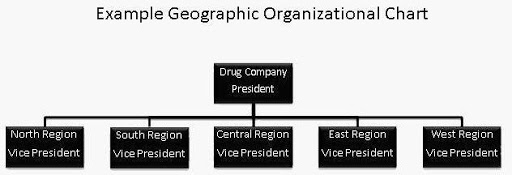
The span of control of a functional manager in Age UK is all the employees performing that particular function. For Virgin Atlantic Airlines, the span of power for an area manager is all the employees working in a specific area (Morgan, 2016).
3. explain how their style of organisation helps them to fulfil their purposes
Besides saving time, labour, and money, Virgin Atlantic Airlines and Age UK have specific purposes of fulfilling the organisation’s style.
Virgin Atlantic Airlines operates on four continents on earth. So it needed a structure that could help its operation go smoothly. For a functional manager, it would be impossible to fulfil all the purposes of the company and control all employees working underneath. Multiple heads do it in geographic structure. When an area manager is appointed in the area only, that particular area manager will have profound knowledge about the business environment and business types (Gimenez 1-16, 2014). So that the area manager will be able to control business more efficiently than other functional heads or customer’s heads, when a manager is efficient and understands his job correctly, he can achieve anything. Starting from the strategy development, area managers of Virgin Atlantic Airlines help in profit maximisation and growth.
But Age UK is not large enough to go for multiple heads in multiple areas. Its operation is only in the UK. So the company heads are already aware of the business environment and changes. So the company believes in functional managers. Age UK believes in specialisation. The operational charges are specialised in different functions. When someone takes over a particular job only, the efficiency increases a lot, according to the division of labour theory. The purposes of the business are excellence in service and compliance with government rules. The functional heads control all the employees efficiently, working under them to fulfil all the necessities (Hsieh, 2010).
4.1 describe the influence of two contrasting economic environments on business activities within a selected organisation
Virgin Atlantic Airlines operates in Egypt and the UK. The UK is a developing country, and Egypt is a developing country. The stability and growth of the UK help the company to run smooth business activity in the country. But the recent recession in Europe also compelled the business to reduce its operation. The same things happen at the time of turmoil in Egypt. Investment in the country is not safe, and return is not always promised. Credits are easily available in the UK. But the cost is high. The opposite is in the case of Egypt. The country has less cost but lower availability. High labour cost in the UK compared to Egypt increases the cost of businesses in the UK. Political turmoil and change in power also bring changes in Egypt frequently. The situation keeps investors worried (Cullen,2016).
The demand and supply of airline services to Egypt is lower compared to the UK. Where most of the UK people make regular journeys by air, Egypt has few people to afford a ride on a plane. But tourist flow to the country keeps the rate high. As people in the UK search for excellence, branding affects businesses here more than in the UK. By creating broader space for businesses, local governments are losing power over international companies. So businesses are freer to operate and get into company formats more to capture the facilities provided by local and international authorities.
4.2 describe how political, legal and social factors are impacting the business activities of the selected organisations and their stakeholders
Government instability will hamper both businesses Virgin Atlantic Airlines and Age UK. But Virgin Atlantic Airlines will be more affected as its investment will come to a halt. On the other hand, being a charity Age, the UK needs less investment and customers come to its necessity, not for luxury. So it will get affected less. Virgin Atlantic Airlines will have to change its strategy of cutting down cost at the time of instability. In the case of improvement from political sides, like the allotment of transportation, education training and research charity organisation Age UK will be benefited more. Government facilitates funds intentionally to bring more services to citizens (“Crystal Structure Of Human GABAA Receptor ”, 2014). But for having a flexible strategy, Virgin Atlantic Airlines will also be able to catch provided facilities.
Legal affairs like protecting consumers and the environment are the demand from the changing world. The businesses are made liable here and compelled to curve operations. Fossil fuel burning by the planes of Virgin Atlantic Airlines is in the protest. So laws here will affect Virgin Atlantic Airlines more. On the other hand, government and pressure groups will keep the business environment free for charities, as it is ultimately helping them without any profit. Legal affairs like ensuring an honest and fair business policy might affect the strategy of Age UK. Legal pressure will also change the system for introducing green business (Caprotti 163-174, 2012).
The population of European countries is reducing, and the economic condition of Asia and African countries are improving. For this reason, Virgin Atlantic Airlines may need to shift their businesses to Asia and Africa from Europe. Furthermore, the education rate and people’s preference to get an education from Europe will also pass in the developing countries for the airline business. In addition, a reduction in gender discrimination will make the company employ more female employees.
Conclusion
Virgin Atlantic Airlines and Age UK are two different organisations but have similar goals: performing better. They have selected their paths according to their operational activities. The ground of operations of the two businesses affects them with economic, political, legal and social environments. The enterprises are facing difficulties and using opportunities by creating their organisational structures.
References
Atkinson, Karen J and Kathleen M Nilles. Tribal Business Structure Handbook. [Washington, D.C.]: Office of the Assistant Secretary-Indian Affairs, 2008. Print.
Caprotti, Federico. “Environment, Business And The Firm”. Geography Compass 6.3 (2012): 163-174. Web.
Cherunilam, Francis. Business Environment. Mumbai [India]: Himalaya Pub. House, 2010. Print.
“Crystal Structure Of Human GABAA Receptor”. Science-Business eXchange 7.26 (2014): n. pag. Web.
Cullen, Deirde. 2016. Web. 18 Apr. 2016.
Gimenez, Julio. “Multi-Communication And The Business English Class: Research Meets Pedagogy”.English for Specific Purposes 35 (2014): 1-16. Web.
Grob, Eva Mira. Documentary Arabic Private And Business Letters On Papyrus. New York, N.Y.: De Gruyter, 2010. Print.
Hsieh, Tony. Delivering Happiness. New York: Business Plus, 2010. Print.
Mitra, Subrata Kumar and V. B Singh. When Rebels Become Stakeholders. New Delhi: Sage Publications India, 2009. Print.
Morgan, jacob. “Forbes Welcome”. Forbes.com. N.p., 2016. Web. 3 Apr. 2016.





