Introduction
Nowadays, it is a prevalent scenario that a business organisation often acquires another business organisation or two business organisations merges to one entity. The objective of this merger & acquisition is to strengthen business function to achieve synergistic gain. This report will analyse the acquisition of Unilever’s soy-based beverage business by coca-cola from different angles that it signed recently.
Merger and Acquisition
One plus one is equal to three is the main reason behind the merger and acquisition (M & A). The value of two companies together is more than that of two individual companies. When a company buys or takes over another company, this special purchase can be defined as the Acquisition. Still, in the case of a merger, two companies agree to go forward under the same name for the competitive advantages (J.M. Ramanuj, 2012). The main reason to go for the M & A is to acquire more efficiency, more significant market share and more significant profit. M & A occurs when a company faces difficulty in adopting the market, or the competition goes very high. The Five stage model is shown in Appendix 1
Selected phenomenon
Coca-Cola acquired Latin American Soy Biz with a payment of $ 575 Million.
Background
AdeS is a leading brand of Unilever that sells a soy-based beverage in Latin America, founded in 1988 in Argentina. It is the biggest soy beverage brand in Latin America, and they also sell fruit juice and milk along with the beverage. AdeS sells its product in Latin America, and its target market includes- Argentina, Mexico and Brazil. This brand reported a profit of $284 million in the year 2015. The Coca – Cola Company and Coca – Cola FEMSA has an agreement to acquire AdeS for the competitive advantages (soda, 2016).
Analysis of the acquisition
Strategy/ Rationale/ context
Optimising the current portfolio of the business structure and determining the changes in M & A can be defined as the corporate strategy. Changing the interest of shareholders after M & A is essential to the concern of the corporate system (Appendices 2)
AdeS is a leading brand of Latin America, selling 56.2 million unit cases of beverage in 2015. The reported profit was $284 million. That is not significant enough compared to the profit of Coca – Cola which is about 40 billion in 2015. But by acquiring the most leading company in Latin America, Coca-Cola can ensure the highest possible revenue. The acquisition cost is $ 575 Million that Coca can recover – Cola within three years if it is possible to continue or hold the current profitability of the AdeS brand. The product ranges are different for Coca – Cola and the AdeS. So, by acquiring, it is possible to capture the whole Latin American market – Argentina, Mexico, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, Chile, Colombia and Bolivia. So, the revenue creation of this acquisition is very high (soda, 2016).
Another part of the corporate strategy is value creation (Das, Raskhit and Debasish, 2009). AdeS’s main product is a soy-based beverage with fruit juice and milk. AdeS is the first company in this field, and it is the second biggest company in the world in this field. So, it is possible to add value to the beverage industry by acquiring such a big brand. For Coca – Cola it is a new milestone. So, from the viewpoint of value addition, it is a good deal. The required expenditure to acquire the AdeS amounts to $575 million. But the value addition from this acquisition must exceed the costs.
The last part of the corporate strategy is future potentiality. As Coca – Cola acquired a giant company in Latin America; it will be tough for the newcomers to compete with Coca – Cola. By this acquisition, portfolios of Coca – Cola become strong, and innovation in food and nutrition can come quickly (MarketWatch, 2016). Future potentiality is high on this acquisition with the increased sales, innovation, advanced technology and dimensional products.
Situation (Buyers wheel / why is the target in play)
Quantification of the acquisition discounted cash flow analysis, and multiples are part of the situation analysis (appendices 3)
AdeS is a unique brand in the beverage industry, and working together with Coca – Cola unleashes its full potentiality. The benefits of the acquisition will exceed the costs of the purchase. AdeS is an established brand, and it has a separate and distinct market share. By acquiring, it is possible to adopt this market. Suppose we quantify the total benefits of the acquisition from market share, future potentiality, growth opportunity, technological advancement, product diversification. In that case, it will exceed the amount of $ 575 Million.
Coca – Cola Company is a leading brand globally, but in Latin America, the pioneer of soy-based beverage is AdeS. Coca – Cola targets AdeS to control the overall beverage industry and provide all the possible products under the same head. With this acquisition, it is possible to prevent the whole Latin American beverage industry from potential consequences. By this acquisition, Coca – Cola has a solid foundation to expand the business to other countries in Latin America. Innovative products in the beverage industry will come automatically as the two leaders come together. By the acquisition, it will be possible for Coca – Cola to control the whole market with diversified products (MarketWatch, 2016).
Last year profit for the AdeS was about $284 million, and it takes less than three years to cover the overall expenditures of $ 575 million. If we discounted this amount, it would be around 2.50 years to cover all the spending. So, from this viewpoint, this acquisition is a successful one.
Valuation / pricing / financing
When coca-cola decided to acquire AdeS it had to reassess the overall value of the acquisition and apply different valuation techniques to determine the actual value of the investment. The valuation process involves analysing the future cash flows, current asset and liability position, contingent issues, etc. and applying different project appraisal techniques. The deal structuring and the negotiation process is a complex and time-consuming process. Experts are taking part in the valuation process, and experts include investing organisations, accountants, legal representatives, etc.
After the acquisition, coca-cola is serving the current products of AdeS, and such products will be offered as their last name. Product pricing is always challenging since setting a product price is subject to various considerations. Customer’s demand, choice, purchasing capacity, desires, etc., so many factors influence the pricing decision. Pricing should be in a way that can restrict the possible entrance of competitors in the target market and create an opportunity for the new market (Das, Raskhit and Debasish, 2009). Coca-cola will set the price by analysing such factors and make its value not only for the customers but also for all related stakeholders. Generally, pricing strategy follows the following matrix:
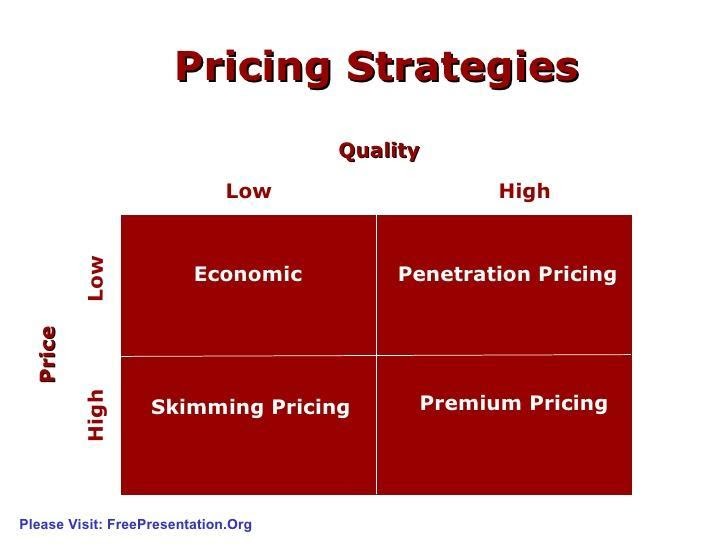
In the case of economic pricing strategy, organisations charge a lower price with low product quality. The problem with such pricing is that lower quality can’t satisfy customers’ needs. As a result, a long term negative impression can be generated among the customers.
Market penetration market strategy is a pricing strategy that can deliver higher product quality at a lower cost to the targeted customers. Profit is reduced through this strategy, but customer satisfaction is achieved (Hitt, Harrison and Ireland, 2001). This strategy can be very effective for coca-cola to set the price for Ades’ products.
Skimming pricing is a less effective pricing strategy where the price charged is higher with a lower quality product. Premium pricing strategy is generally used for unique quality products.
The necessary funds and to continue the post-acquisition operation, coca-cola needs to arrange more than $575 million, which is considered a considerable investment. The sources of such funds and the fund’s costs significantly influence the acquisition decision (Gates, 2000). In most cases, the funds come from the issuance of new shares, bank loans, investing funds, cash funds, etc., shareholders’ dividend, and the interest costs are the cost of capital for such sources of funds. Financing decisions are shaped by considering different sources of funds and their associated costs (Gleich, Kierans and Hasselbach, 2010).
Post-transaction integration
Every merger and acquisition considers the post-transaction effects. After the purchase of AdeS, coca-cola will achieve a new hierarchy of authority, and the management structure will be changed as per the authority decision of coca-cola. The organisation culture and environment will be changed as the new administration will control the organisation. The new management team members will influence the decision-making process, strategic decision, reporting system. People in every level of management and their behaviour are affected by the takeover of the acquisition firm (Sudarsanam, 2010).
One major problem with the acquisition is the value creation after the post-acquisition period. Coca-cola now needs to consider how they will add value to the existing beverage products of AdeS so that their market reputation can be strengthened. A detailed strategy and to implement the system, a roadmap needs to be created, and both the organisations need to agree on that issue (Gleich, Kierans and Hasselbach, 2010). For this purpose, market segmentation, target market, potential customers need to be specified.
The future growth opportunity for the acquisition is very high since other competitors of the Latin American market will face fierce competition from such a significant acquisition. Since Coca-cola has a strong brand value and reputation serving such a long time in Latin America and in the whole world, it will be easier for them to accelerate the sales of AdeS products by using their strong distribution channel vast experience. By offering non-carbonated beverage products, coca-cola will be offering nutritious products, which will create a new dimension for coca-cola adding a new portfolio to their existing product groups. Alternatively, existing competitors may pressure the newly acquired business by launching a new marketing strategy to sustain itself in the market (Sudarsanam, 2010). Coca-cola needs to assess the competitors’ position and their capacity.
Another concern for the post-acquisition period is to increase the value of the shareholders. How AdeS acquisition will accelerate sales and contribute to the profit margin must be considered before the purchase. The shareholder will look at the organisation’s financial performance and position in the end (Sudarsanam, 2010). So in the post-acquisition period, how coca-cola will create value for their shareholders needs to be addressed and proved.
The essential sources of finance after the acquisition for the capital expenditure like infrastructure development, plant, transport facilities and the continuing operation of purchasing materials, labours, administrative expenses, etc., need to be ensured (Gates, 2000). To accelerate the sales growth and capture market essential investments and their costs must be considered.
The price of the product offered and the capacity to purchase is also important that the organisation needs to deal with. Since coca-cola will provide the existing products of AdeS and most of the products are beverage products, the price determination for the product is a vital issue. Competitor’s price and quality assessment can be fruitful in this regard.
Conclusion
Coca-Cola’s acquisition of Unilever’s soy-based beverage business is analysed for different viewpoints in the above report. The analysis mainly covered the four broad areas where the acquisition is expected to add value for the coca-cola shortly and ensure sustainable growth. As mentioned by coca-cola CO, James Quincey, “We expect to continue to grow faster in stills … and we’ll continue to look for acquisitions to accelerate our growth.”
References
Das, B., Raskhit, D. and Debasish, S. (2009). Corporate restructuring. Mumbai: Himalaya Pub. House.
Gates, S. (2000). Performance measurement during merger and acquisition integration. New York, NY: Conference Board.
Gleich, R., Kierans, G. and Hasselbach, T. (2010). Value in due diligence. Farnham, Surrey [U.K.]: Gower.
Hitt, M., Harrison, J. and Ireland, R. (2001). Mergers and acquisitions. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
J.M. Ramanuj, J. (2012). Introduction of Merger, Acquisition and Divestitures. PARIPEX, 3(6), pp.132-134.
MarketWatch. (2016). The Coca-Cola Company and Coca-Cola FEMSA to Acquire AdeS Soy-Based Beverage Business From Unilever. [online] Available at: http://www.marketwatch.com/story/the-coca-cola-company-and-coca-cola-femsa-to-acquire-ades-soy-based-beverage-business-from-unilever-2016-06-01-91601312 [Accessed 16 Jun. 2016].
soda, C. (2016). Coca-Cola just made a $575 million departure from soda. [online] Business Insider. Available at: http://www.businessinsider.com/coca-cola-acquires-ades-for-575-million-2016-6 [Accessed 16 Jun. 2016].
Sudarsanam, P. (2010). Creating value from mergers and acquisitions. Harlow, Essex, England: FT Prentice Hall.
Appendices
Appendix 1
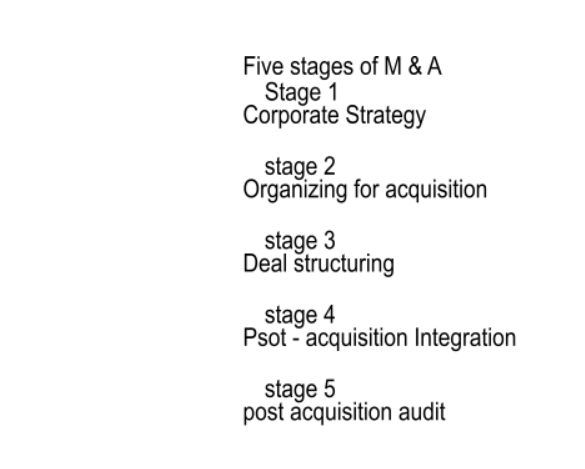
The above stages are interconnected and execution of one stage only helps to start the next stages. The main reason to go for five stage analysis is to know the overall success and failure of the M & A.
Appendices 2

Appendices 3






