1. Introduction
In this part, the researcher will discuss the research’s essential background and show why he has selected this research topic.
1.1 Background of the research
While doing the business, the organisation needs to communicate with the customers to inform the customers regarding its offering. So it is a crucial issue to be considered carefully in case of choosing the promotional strategies. Though there are many ways to communicate with the customers, organisations should focus on a system that can meet the customer’s requirements and the organisation. But still, now there are many confusions about which promotional activities are better for the organisation. The best strategy can influence the behaviour of the customers to a broader extent. So the marketing communications strategy is a critical issue for the organisation (Cosmas, 1992).
1.2 The rationale of the research
As the issues arise regarding marketing communications, the researcher will show how these marketing communications help the customers positively. So the topic selected for this research mainly focuses on the different strategies of product promotion. The business organisation’s primary focus s to capture more customers through strategies like promotional strategies, marketing strategies, marketing mix, etc.; whatever the organisation takes the system, the essential purpose is to capture more customers and bring in more customers from other organisations. So, the major problem is whether the customers are responding properly as expected before implementing the promotional activities. So, the researcher will be focusing on all of these issues, considering which marketing communication strategy or promotional strategy is persuasive that can overwhelm the customers and make them regular customers. Here, the significant factors that can make the customers aware and bring them to the shop for buying the products will be the critical point of the research.
1.3 Aims of the research
This research aims to discover the different marketing communications strategies and determine how these marketing communications shape the customers’ behaviour. So, the aim will be to find the most prominent factor contributing more to the promotion of the products and change the customers’ behaviour.
1.4 Objectives of the research
The objectives of the research are;
- To critically analyse the different marketing communications strategy made by Coca Cola.
- To find out the most influencing factor of the marketing communication for Coca Cola.
- To find out the effect of the marketing mix on the behaviour and perceptions of the customers.
1.5 Research questions
The research questions for the research project are;
- What are the different marketing communications strategies made by Coca Cola?
- What are the most influencing factors of the marketing communication for Coca Cola?
- What is the effect of the marketing mix on the behaviour and perceptions of the customers?
2. Literature review
The researcher showed the different theories and literature related to the research project. Here the researcher analysed different strategies for better marketing communications and promotion.
2.1 Promotional strategies
While doing the business, all the organisation has to follow some promotional strategies to capture the customers by informing them and realising the key features of the products. Here a customer makes the buy decision typically in the following stages;
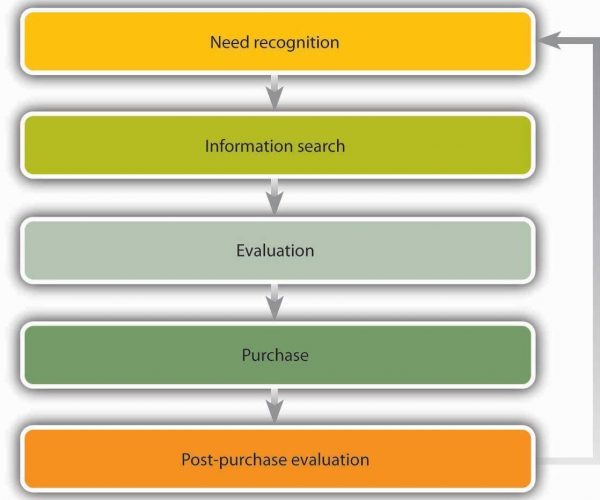
Here the customers first identify needs before searching for the products. But the strong marketing and promotional strategies can create conditions among the customers though they were not intended to buy that product (Pamela, 1986). According to Ksynsk and Kara (2001), if customers get the correct information quickly about the company’s products, the customers will be willing to buy that product. So a good promotion should be made to make the customers understand regarding the products. So, the proper promotional strategies will influence customers’ buying behaviour (Leslie et al., 2012).
2.2 Marketing Communications Mix
Before making the proper strategies, the marketers strive to influence how prospective customers think. For this reason, we need to understand how and when to guide the customers properly. So, here a potent marketing communications mix does the following task to help the customers with the buying decision (Hoyer and MacInnis, 2010). The customers are aware of the products just because of the company’s good marketing communication policies and promotional strategies. Then marketing communications help hook the customers and engage them to become interested in buying the products (Solomon, 2010). Belk (2010) also said that making the customers interested in purchasing the products is not the main thing the marketing communication should be in such a way so that they make the final decision for buying the products. For this reason, the most used marketing communications mix are shown in the following figure;
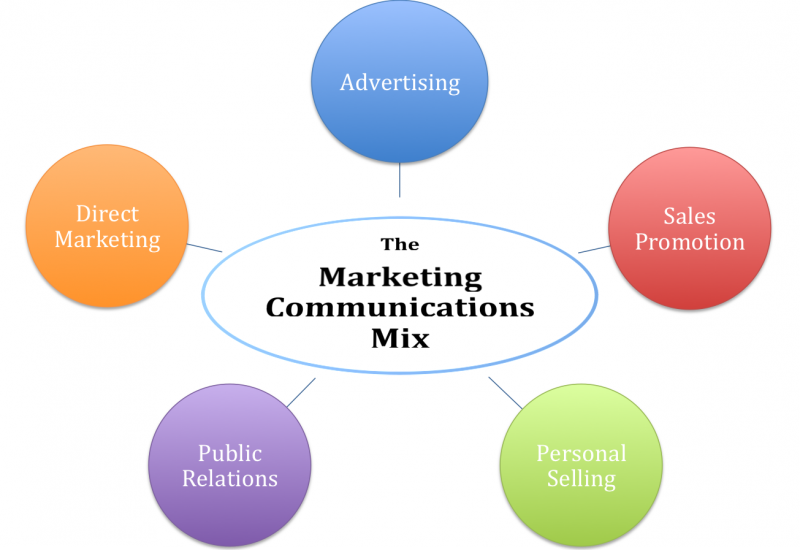
Here, all of these strategies taken by the firm are commonly used in different organisations. These are analysed critically in the following;
2.2.1 Advertising
In modern electronic media, the most widely used promotional strategies are used by almost all firms in advertising, through which the firm can easily capture a lot of customers within a short time (Foxall, 2009). On the other hand, Vanhuele and Wright (2008) stated that advertisement is the most effective marketing communication policy where the marketer tries to provide a short overview of the products conveniently and excitingly so that it can successfully make a place in the customer’s mind. In marketing communication, the strategy’s primary purpose is to make good communication where the customers will get all the information quickly about the company’s products. However, Jamal (2009) argued that advertisement just provides the product’s statement to the customer, but it cannot influence them to make their buying decisions. For these reasons, other communication mixes are required to change the attitudes of the customers.
2.2.2 Sales promotion
Promotional strategies are taken for the short term sales increase for the firm. In the recent competitive market when customers are normally exposed daily to a lot of promotional messages and options, many business organisation and firms have found that advertising alone is not strong enough to move customers of a target market to make buy decisions, such as influencing them to buy a new product (Parsons and Maclaran, 2009). For these reasons, the other promotional strategies are required as advertisement alone cannot meet all requirements. Here, the sales promotion can suddenly increase the firm’s sales volume, but this increase is not for the long term (Khan, 2006). Swanson (2011) added that the sales promotion could be in two ways like trade sales promotion and consumer sales promotion, where the firm has to find out which one is more appropriate.
In the trade sales promotion, different techniques are used like the schemes, freebies, commissions, discounts, and incentives are given to various retailers or wholesalers to buy more, stock more, push more and sell more so that they can maximise their profit level (Leslie et al., 2012). However, Hoyer and MacInnis (2010) argued that the sale promotion should be for the final consumers. The consumers will be happy to have such promotional benefits as discounts, gifts, and game shows. Solomon (2010) also added that if the sales promotion is done for the final consumers and the promotional activities are more exciting, they will be loyal. Its effect will be for a long time.
2.2.3 Personal Selling
Though almost all organisations try to promote the products to the customers through advertising and other ways, the person selling has a future effect on the organisation. According to Khan (2006), the relationship with the customers can quickly be established with the customers. Still, the face highly influences personal selling as face-to-face communication rather than virtual communication like TV advertising and other media communication. Alford and Biswas (2002) also said that the objectives of personal selling are to increase sales and make a good relation with the customers and inform them about the company’s products. Fantini (2011) stated that buying something is when the buyer has to decide between different opposing tendencies and options. There is a strong desire for the object and proper reasons lined up to support a Yes. The buyer has suitable ground and reasons to say yes or no for buying the products. However, David and Martina (2008) helped that personal selling is the best way to persuade the customers to buy the products. So, personal selling can successfully convince the customers to purchase the products and make good relations with the company (Entrepreneur, 2014).
2.2.4 Public relations
In every case, the relationship with the public matters as the people usually prefer those with a good relationship and maintain good communication properly. According to (Keller, 2001) if two companies are offering the same products with the same value, the customers will generally prefer those products provided by the company that maintains a good relationship with the customers. On the other hand, Donut (2014) stated that customers’ buying behaviour is affected by few factors like personal attitudes, cultural and social trend, family, psychological issues etc., where the relationship with the customers can change the motive of the customers and induce them to buy the products.
2.2.5 Direct Marketing
Direct marketing means making direct contact with different existing and potential customers to promote the products or services. Direct marketing is more effective in cost and other benefits, where direct marketing targets a particular customer and offers unique gifts for the customers. Different techniques for the direct marketing are shown in the following figure;

Direct marketing communicated with the customers directly and offered them some products with special offers; then, the customers decided to buy the products as direct marketing easily persuaded them to purchase them (Mowen, 2000). On the other hand, (Hanson 2007) stated that direct marketing could easily capture customers as it communicates with the customers and provides information.
Here, the firm or organisation sends direct offers to the customers through email, SMS, phone calls etc., where the customers are considered to respond positively. However, it cannot reach all customers as direct marketing is usually done for some selected customers, unlike advertising.
2.3 Customer Buying behaviour and processes
Customers decide to buy a product after a lot of considerations and analysis. Here, the customers typically buy those adjusted products with social trends and culture, psychology, etc. So, the behaviour of the customers should be influenced before deciding to sell the products to the customers properly. According to Fantini (2011), the essential thing in the promotional activities is to make the customers aware of the products the company is offering where the customers will consider further steps if they are aware of it. Typically buying decisions go through different stages, from the need recognition to the pre-purchase evaluation. So, in every scene, the marketing communication strategy or mix contributes to influencing the customers.
According to David and Martina (2008), the marketing mix has to inform the customers in such a way so that the customers can realise that they were looking for such kinds of products. Khan (2006) also said that the new demand among the customers could be created through effective communication and promotional policies. So, after completing the needs among the customers, the information should be available so that the customers can find the products quickly and know them in detail. Furthermore, the marketing communication mix will help the customers decide and help them select the best products suitably.
So, the conceptual framework for this research will be like the following;
Dimensions | Description |
Advertisement | It is used to capture many customers within a short time, providing the information to the customers. |
Sales promotion | A sudden effort to increase sales through different offerings and rewards for the customers and retailers. |
Personal selling | It is used to increase sales through the personal link and increase the relation with the customers to influence the customers’ behaviour. |
Public relation | It is widely used to make a good relation with the customers as customers become loyal and believe in the products offered by the company. |
Direct Marketing | Products are sold to the customers through direct marketing like email, phone call, SMS etc. It is more cost-effective for the firm to sell the products. |
Perception of the customers | All of the marketing communications mixes are used to influence the perception of the customers and to create a positive attitude among the customers for the products offered by the firm |
Buying behaviour of the customers | The marketing communications mix affects the behaviour of the customers in every step of the buying process. |
Table 1: Conceptual framework
Source: made by the author.
From the above conceptual framework, the researcher has developed the following research paradigm;
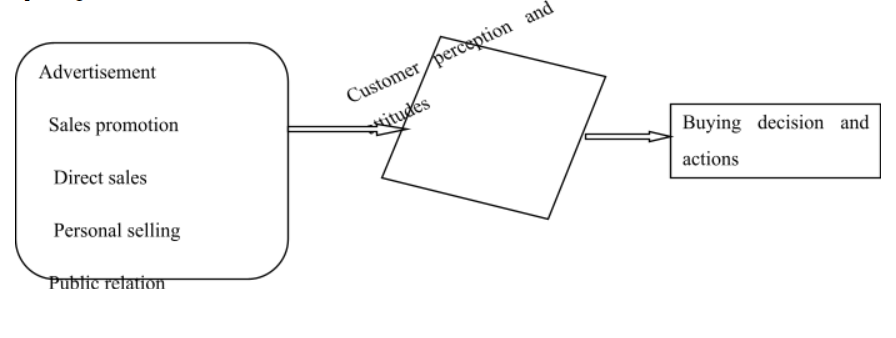
From the above research paradigm and conceptual framework, it can be said that the proper marketing communications mix can change the attitudes of the customers and their perception. Then, the customers make the buying decision based on the perception built from the different promotional strategies and marketing communications mix (Belk, 2010). The researcher will apply this to coca-cola to determine how coca-cola influences the customers and their buying behaviour through the marketing communications mix and other ways. As the branding and communication strategy made by the coca-cola is quite different from other companies, the researcher aimed to find how these innovative communications mixes affect the behaviour of the customers and how they make decisions for buying the coca-cola based on these factors.
3. Research Methodologies
While doing the research, the researcher follows some methods and proper ways to complete the analysis that depends on the research topic and other factors like the estimated time for the researcher, cost, knowledge, and available data (Statpac.com, 2014). For this research, the researcher will follow the different methods discussed in this section.
3.1 Research Approach
Inductive research Approach: In inductive research, the researcher does the research project considering some assumptions then tries to build a theory that can represent the actual situation. Here, the researcher collects the data, then makes some hypothetical assumptions then applies the premises to the real problems to make a theory. So, under the inductive approach, the researcher first makes a hypothesis based on the assumptions, collects data, and tests whether the idea is right or wrong. Finally, the researcher does not know what will be done in the inductive research approach, but he just tries to make a new theory or do the same previously built idea from a different perspective (Dudovskiy and Dudovskiy, 2014).
Deductive Research Approach: in this approach, the researcher collects the data to find out whether the theory exists, and the researcher does not make any assumptions; instead, he tries to confirm the theory or hypothesis in the practical world. Here, the researcher chooses a specific idea or view for the data collection to ensure that the thesis or belief is based on natural ground. This process for both the inductive and deductive research approach is shown in the following figure;

In This Research project, the researcher will use the deductive approach to collect the numerical data. He will try to find out whether marketing communications effectively change the customers’ perception. So, as the researcher will consider a previous theory and work on it, the researcher will use the deductive research approach.
3.2 Research methods
Research methods are used for the data analysis that depends on the type of the research and its data collection and analysis process. There usually are two types of research methods that are discussed below;
Quantitative research method: Quantitative research method is typically used in deductive research methods. The researcher has to collect the data in numerical form, and the researcher goes for the specific result instead of theoretical analysis (Gibaldi, 2009). In the quantitative method, the data are collected properly. The development of the research is made based on the proper mathematical analysis where the researcher can provide the appropriate logic of the study based on the result found through using different tools like mean, median, mode, correlation, regression etc. (McDaniel and Gates, 2005). The quantitative method is more specific than other methods like qualitative methods and mixed methods.
Qualitative research method: The researchers research qualitative data and information instead of numerical data. Here, the researcher works on assumptions where the assumptions made may differ from real situations (Sontakki, 2010). No, specific result is found here; instead, the researcher just provides the guidelines and assumptions for the analysis. Most of the time, this kind of research is made for the inductive research approach where the researcher does the study based on some hypothesis (Turabian, 2007).
Mixed Research Method: when the researcher does the research based on qualitative and quantitative methods is called the mixed research method. Here, the quantitative and qualitative data are collected for the analysis, and the researcher uses the questionnaire, interview and other methods for the data collection (Mallette and Duke, 2004). The researcher uses this method when the researcher thinks that the data will be collected from numeric and non-numeric sources. The research needs some assumptions and precise analysis.
In this research project, the researcher will use the quantitative research method. The researcher will collect the data through the questionnaire and use the numerical data in numerical forms. On the other hand, the researcher will use this method to use the deductive research approach and other tools for the data analysis. So, this method will provide a better result for the research project.
3.3 Data Collection
The researcher has to collect different data from different sources that depend on research methods and approaches in the research project. The data collection methods are discussed below;
Primary sources of Data: Primary data is in discrete forms that need to be collected through questionnaires and interviews (Noble and Bestley, 2005). This source of information is more costly and requires more time to collect the data. On the other hand, the collected data needs to sort and classify according to the desired uses. Here the researcher emphasises on perfectness and accuracy of the data.
Secondary sources of data: This source is used when the researcher uses the already published data from other sources. This is a straightforward and less costly source of data collection, but the researcher must be more careful in this case as the data may not be appropriate for the research due to the time, unit and other reasons (Chilisa, 2012).
In this research project, the researcher will use primary sources for the data collection. The researcher will use the questionnaire and collect the different coca-cola customers living in London, UK. The researcher will collect these data using the questionnaire on a scale of 7.
3.4 Sampling techniques
This is not possible to work using all the research population as the researcher will not have enough time to do that. So, the sampling is the best to represent the population where there are different sampling techniques discussed below;
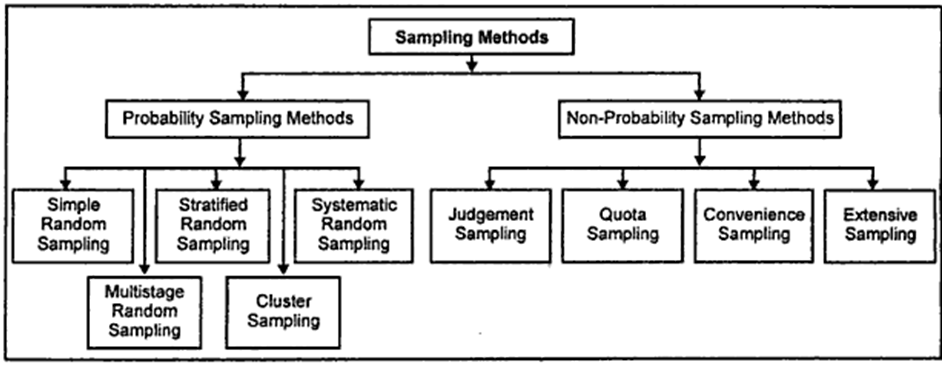
- Probability sampling: In probability samples, it is clear that each member of the population has a probability of being selected, and there is no probability of being excluded from the model. Different probability methods include random sampling technique, systematic sampling technique, and stratified sampling.
Random sampling is probability sampling, where every member or respondent of the population has an equal probability to be selected as the population is chosen randomly. This is used in the case of a large population. On the other hand, systematic sampling is used instead of random sampling when the researcher wants to collect the data using the systematic method like selecting every nth population from the sample list. This is simple and easy to use. On the other hand, Stratified sampling is also a commonly used probability sampling method where a stratum is a subset of the population that share at least one common characteristic. This method is used for fewer errors where the researchers use it to collect the data from the selected sample like female or male (Saunders et al., 2009).
- Non-probability sampling: In nonprobability selection, the sample is collected considering a specific group in some non-random manner. Some non-probability sampling methods are convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgment sampling, and snowball sampling. In the convenience sampling technique, the researcher is interested in getting an inexpensive approximation of the truth for the research. In quota sampling, the researcher uses some quota based on the population for the data collection. Finally, snowball sampling may be used if the sampling characteristic is quite different from others, and the researcher has to apply some unique method (Noble and Bestley, 2005).
In this research, the researcher will use probability random sampling, where the researcher will collect data from coca-cola customers. The demographic area of the study will be London, and the age and race will be from different dimensions where all the consumers will be given priority. The researcher will collect the data from a sample of 100 respondents and will collect data using the questionnaire from these respondents.
3.5 Ethical consideration
The researcher will maintain complete ethical issues so that the respondents and other parties related to the research do not face any problems in the future. Here the collected data from the respondents will not be disclosed to other parties without the respondents’ consent. On the other hand, the researcher will not do anything that may create problems for the respondents. However, the researcher plans to do this research only for academic purposes, and there is no other intention behind it. Finally, all the data collected will not be changed for the researcher’s own desired result.
3.6 Limitation of the research
Though the researcher I am using is the best research method and the data will be appropriately collected, the research may face some limitations. The major hurdle that may arise is that the sample used for the study may not be a proper representative for coca-cola as the company has many customers worldwide. Still, the researcher is doing the research using only 100 samples from London. On the other hand, if the respondents do not respond appropriately, the study may be vain. On the other hand, the estimated time for the research is not enough that may create problems to complete the analysis correctly.
3.7 Timeline for the research
The researcher will be researching the following activities;
Activities | Week | ||||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
Proposal review and finalisation | |||||||||
Literature review analysis | |||||||||
Methodology review | |||||||||
Data collection | |||||||||
Data analysis | |||||||||
Findings discussion | |||||||||
Conclusion and referencing | |||||||||
Full report review and printing | |||||||||
Table 2: Time table for the research
Conclusions
This research project will be done considering whether the marketing communication mix of coca-cola affects the customers’ perception and how coca-cola uses their promotional activities to persuade the customers. Here, the researcher will focus on how the different strategy is required to bring the new customers and regularly make them for the organisation. The main focus will be to find how the marketing communications mix affects the customers’ behaviour and its impact on its performance.
References
- Cosmas, S.C. (1992). Lifestyles and consumption patterns. Journal of consumer research, 8: 435–5.
- Hansal, S. (2001). Advertising and marketing strategies: a lifestyle approach. New Century Publications.
- Kahle, L.R. (1984). Values Segmentation Debate continues. Marketing News, 18: 2.
- Kahle, L.R., Sharon, E.B., and Pamela, M.H. (1986). Alternative Measurement Approaches to Consumer Values: The List of Values (LOV) and Values and Lifestyle Segmentation (VALS). Journal of Consumer Research, 13: 203–223
- Ksynsk, E. and Kara, A. (2001). An examination of the relationship among consumer lifestyles, ethnocentrism, knowledge structures, attitudes and behavioral tendencies: a comparative study in two CIS states. International journal of advertising, 20(4).
- Hansen H., Schiffman L.G., Leslie K. (2012) ‘Consumer Behaviour: A European Outlook’,
- Pearson: London.
- Hoyer, W.D. and MacInnis, D.J. (2010) Consumer Behaviour. Mason, South Westen
- Solomon, M.R. (2010) Consumer Behaviour: Buying, having and being. (9th Ed.). Prentice Hall
- Belk, R. (2010) Research in Consumer Behaviour. Emerald Group Publishing Ltd. Online at: http://www.ebooks.com/615842/research-in-consumer-behaviour/belk-russell/
- Blythe, J. (2007) Consumer Behaviour. Bedford, Thompson Learning.
- Foxall, G. (2009) Interpreting Consumer Choice. Taylor and Francis. Online at: http://www.ebooks.com/446800/interpreting-consumer-choice/foxall-gordon/
- East, R., Vanhuele, M. and Wright, M. (2008) Consumer Behaviour: Applications in Marketing. London, Sage.
- Evans, M., Foxall, G. and Jamal, A. (2009) Consumer Behaviour. West Sussex, John Wiley & Sons Ltd
- Parsons, E. and Maclaran, P. (2009) Contemporary Issues in Marketing and Consumer Behaviour. Taylor and Francis. Online at: http://www.ebooks.com/428556/contemporary-issues- in-marketing-and-consumer-behaviour/parsons-elizabeth-maclaran-pauline.
- Khan, M. (2006) Consumer Behaviour and Advertising Management. New Age International Pvt. Ltd., Publishers. Online at: http://www.ebooks.com/418811/consumer-behaviour-and- advertising-management/khan-matin/
- Alford, B. and Biswas, A. (2002). The effects of discount level, price consciousness and sale proneness on consumers’ price perception and behavioural intention. Journal of Business research, 55(9), pp.775–783.
- Chiodo, E., Casolani, N. and Fantini, A. (2011). Evaluation of the effects of changes in regulatory policies on consumers perception: the case of designations of origin in the wine common market organisation. pp.17–18.
- David, S. and Martina, R. (2008). Marketing Communications Mix of Universities-Communication With Students in an Increasing Competitive University Environment. Journal of Competitivenes.
- Entrepreneur, (2014). Public Relations Definition | Small Business Encyclopedia. [online] Available at: http://www.entrepreneur.com/encyclopedia/public-relations [Accessed 2 Jun. 2014].
- Lane Keller, K. (2001). Mastering the marketing communications mix: Micro and macro perspectives on integrated marketing communication programs. Taylor \& Francis.
- Marketing Donut, (2014). Direct marketing. [online] Available at: http://www.marketingdonut.co.uk/marketing/direct-marketing [Accessed 4 Jun. 2014].
- Nku.edu, (2014). Marketing and public relations. [online] Available at: http://www.nku.edu/~turney/prclass/readings/mkting.html [Accessed 1 Jun. 2014].
- Spears, N., Lin, X. and Mowen, J. (2000). Time orientation in the United States, China, and Mexico: Measurement and insights for promotional strategy. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 13(1), pp.57–75.
- Thackeray, R., Neiger, B. and Hanson, C. (2007). Developing a promotional strategy: important questions for social marketing. Health Promotion Practice, 8(4), pp.332–336.
- Statpac.com, (2014). Survey Sampling Methods. [online] Available at: http://www.statpac.com/surveys/sampling.htm [Accessed 1 Jun. 2014].
- Dudovskiy, J. and Dudovskiy, J. (2014).Research Methodology – Necessary knowledge to conduct a business research. [online] Research-methodology.net. Available at: http://research-methodology.net [Accessed 27 May. 2014]
- Gibaldi, J. (2009). MLA handbook for writers of research papers. 1st ed. New York: Modern Language Association of America.
- McDaniel, C. and Gates, R. (2005).Marketing research. 1st ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Socialresearchmethods.net, (2014).Social Research Methods. [online] Available at: http://www.socialresearchmethods.net [Accessed 27 May. 2014].
- Sontakki, C. (2010). Marketing research. 1st ed. Mumbai: Himalaya Pub. House.
- Turabian, K. (2007). A manual for writers of research papers, theses, and dissertations. 1st ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Mallette, M. and Duke, N., 2004. Literacy research methodologies. 1st ed. New York: Guilford Press.
- Noble, I. and Bestley, R., 2005. Visual research. 1st ed. Lausanne: AVA.
- Chilisa, B., 2012. Indigenous research methodologies. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: SAGE Publications.
- Colwell, R., 2006. MENC handbook of research methodologies. 1st ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Saunders et al (2009) “Research Methods for Business Students.5th edition”.England: Pearson Education Limited.





